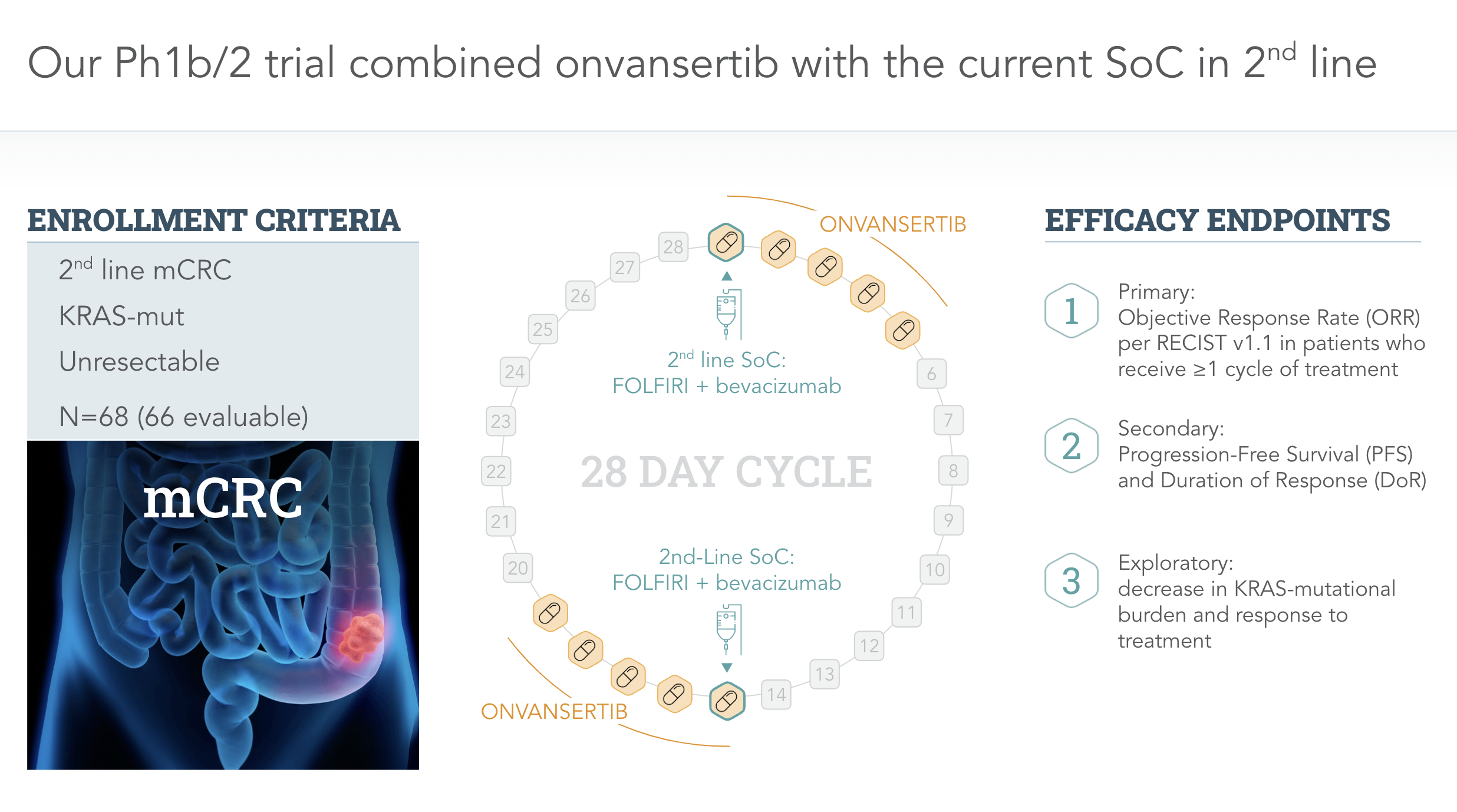
Clinical Programs
Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (mCRC)
Onvansertib in combination with second-line standard of care (SoC) is reducing tumor growth and increasing progression-free survival.
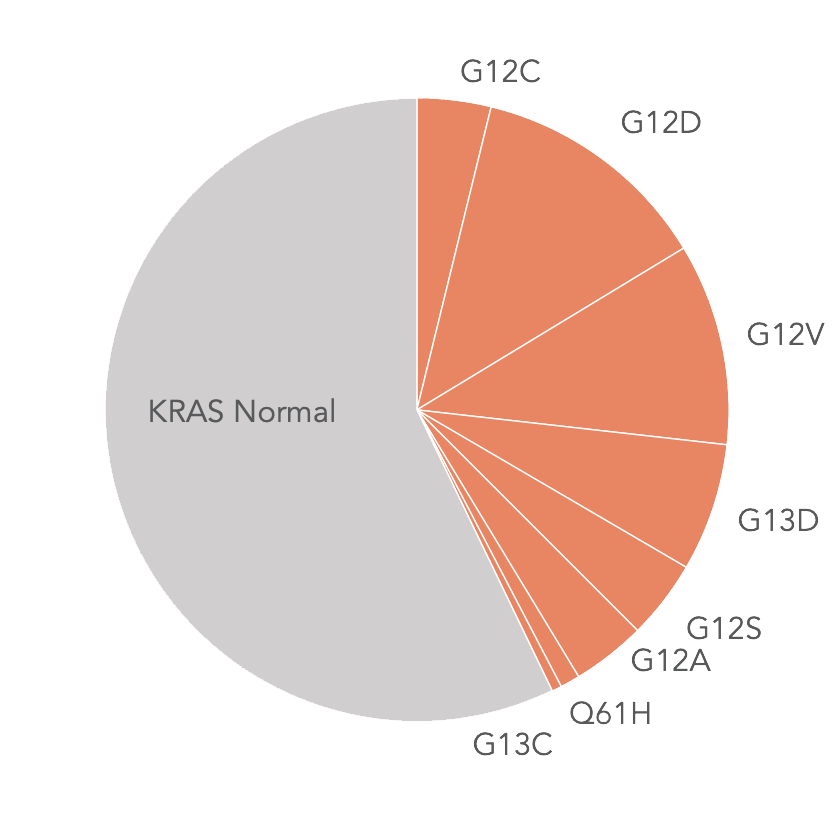
KRAS Mutations in mCRC*
* Jones R et al. Br J Cancer. 2017 Mar 28;116(7):923-929
Gaps in KRAS-mutated mCRC therapies present a significant unmet need
- 40%+ of mCRC patients have a KRAS mutation and therefore do not benefit from targeted therapies (e.g., EGFR inhibitors) in first-line therapy
- Current investigational therapies for KRAS-mutated mCRC from Amgen, Mirati only address the G12C mutation, not the most prevalent KRAS mutations
- Onvansertib has the potential to address all KRAS mutations because PLK1 activation is downstream of RAS
The prognosis for second-line mCRC patients is poor
- For second-line mCRC patients, the 5-year survival rate is 10%
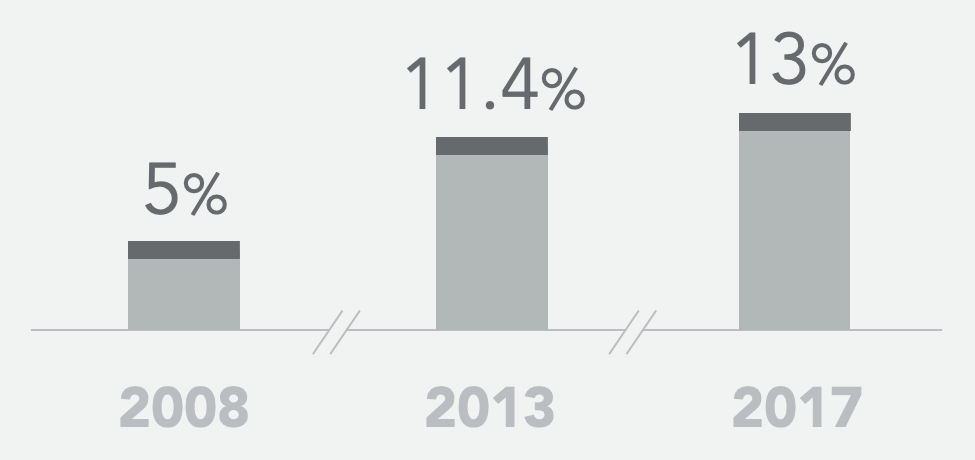
- Historical controls showed a 5-13% objective response rate to second-line standard of care FOLFIRI+bevacizumab and a median progression-free survival of 4.5 – 5.7 months
Historical SoC* ORR
Historical SoC* mPFS (months)
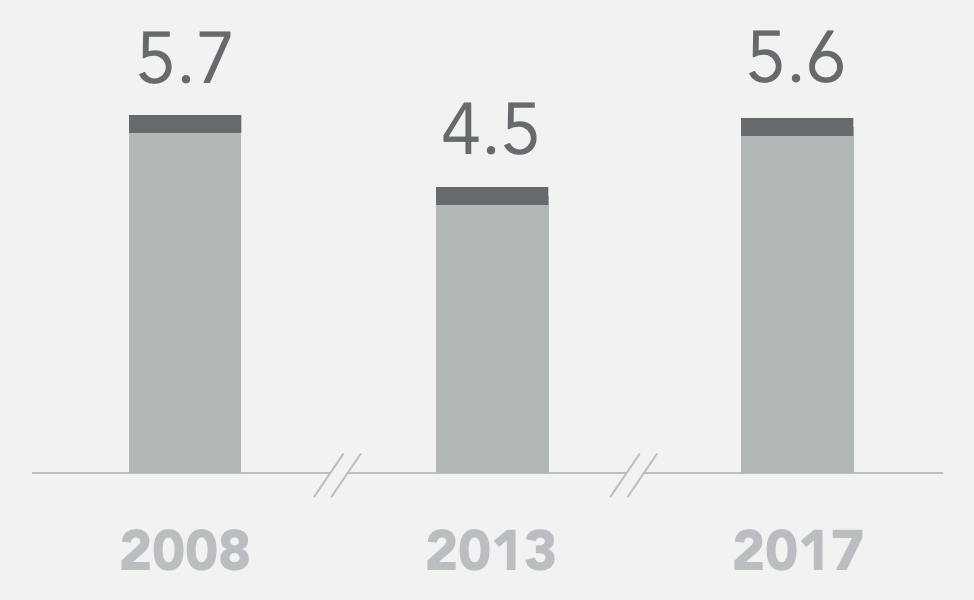
* 2008: Bennouna et al., Lancet Oncol 2013; 14: 29–37; 2013: Giessen et al., Acta Oncologica, 2015, 54: 187-193; 2017: Cremolini et al., Lancet Oncol 2020, 21: 497–507; and Antoniotti et al., Correspondence Lancet Oncol June 2020